Space is full of strange and amazing things that boggle our minds. From mysterious black holes that swallow everything to planets made of diamonds, the universe is full of wonders. Scientists are working hard to study these oddities and understand what they mean. This article will take you on a journey through some of the most bizarre phenomena in space.
Key Takeaways
- Black holes are regions in space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
- Some exoplanets, like ‘diamond planets,’ are made of materials that are rare or nonexistent on Earth.
- Dark matter, which makes up most of the universe’s mass, remains one of the biggest mysteries in science.
- Cosmic rays are high-energy particles from space that scientists are still trying to understand.
- Pulsars are rapidly spinning neutron stars that emit beams of radiation, and they can behave in unexpected ways.
Mysterious Black Holes
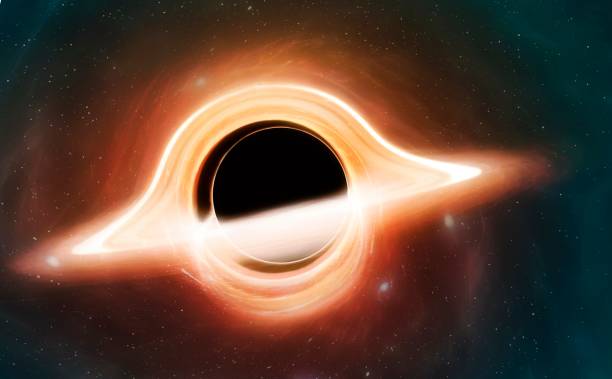
The Event Horizon
The event horizon is the boundary around a black hole beyond which nothing can escape, not even light. Venture beyond the event horizon and you’ll not be able to escape the powerful gravity of a black hole. This invisible line marks the point of no return. Despite their dark nature, black holes can shine brightly due to the hot, glowing material in the accretion disc that swirls around them.
Hawking Radiation
Hawking Radiation is a theoretical prediction that black holes can emit radiation due to quantum effects near the event horizon. This phenomenon suggests that black holes can slowly lose mass and eventually evaporate over time. It’s a fascinating concept that challenges our understanding of these cosmic giants.
Spaghettification
Spaghettification is the process where objects get stretched and torn apart by the intense gravitational forces as they approach a black hole. This dramatic effect is due to the difference in gravitational pull on different parts of the object. It’s a vivid reminder of the extreme conditions near these mysterious entities.
Black holes are objects so dense that not even light can escape their gravitational pull. Yet, they can illuminate the center of galaxies and are known as active galactic nuclei.
Strange Exoplanets
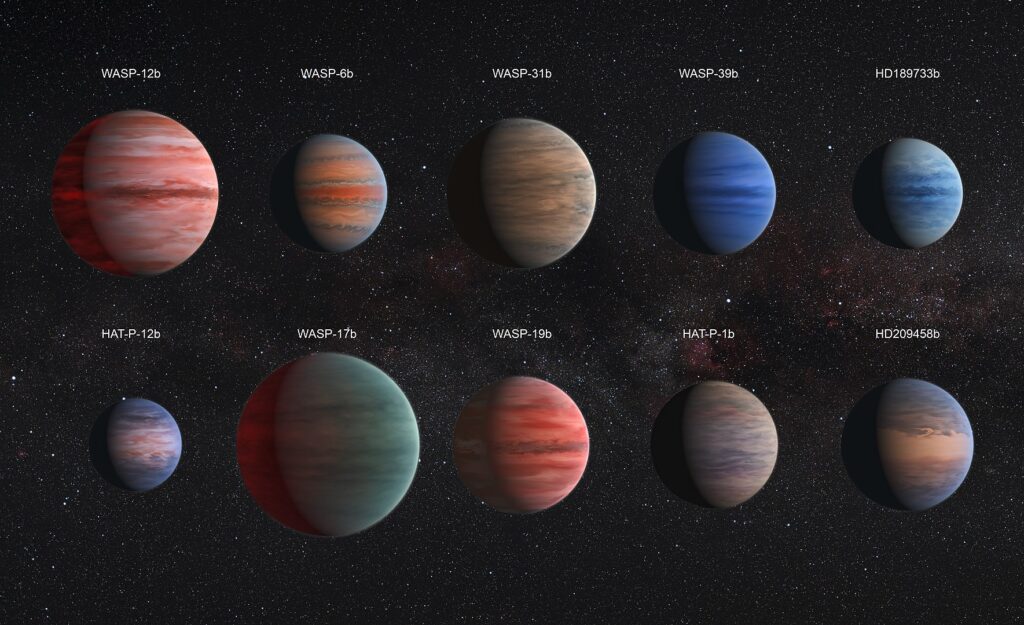

Hot Jupiters
Hot Jupiters are giant planets that orbit very close to their stars. These planets are similar in size to Jupiter but have much higher temperatures due to their proximity to their stars. They can complete an orbit in just a few days, making them some of the fastest orbiting planets discovered.
Diamond Planets
Imagine a planet made mostly of diamond! Some exoplanets are believed to have extremely high carbon content, which under intense pressure, forms diamond. These planets are not only rare but also incredibly fascinating.
Tatooine-like Systems
Named after the famous planet from Star Wars, Tatooine-like systems have planets that orbit two stars. This means that if you were standing on one of these planets, you would see two suns in the sky. These systems are also known as circumbinary planets.
The universe is full of facts about the strangest, weirdest, most unusual and downright coolest exoplanets astronomers have discovered over the past few decades.
Enigmatic Dark Matter

WIMPs and Axions
Dark matter is a mysterious substance that makes up about 85% of all matter in the universe. Scientists have proposed particles like WIMPs (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles) and axions as possible candidates. These particles are hard to detect because they don’t interact with light, making them invisible to our current instruments.
Gravitational Lensing
Gravitational lensing is a phenomenon where light from distant stars is bent around massive objects like galaxies. This bending effect helps scientists map out the distribution of dark matter in the universe. Gravitational lensing provides indirect evidence of dark matter’s presence.
Missing Baryon Problem
The missing baryon problem refers to the discrepancy between the amount of normal matter we can see and the amount we expect to find. Dark matter might help solve this puzzle by accounting for the unseen mass. Researchers are still trying to figure out how dark matter and dark energy shape the cosmos.
Dark matter and dark energy are mysterious substances that affect and shape the cosmos, and scientists are still trying to figure them out.
Unexplained Cosmic Rays
Ultra-high Energy Particles
Cosmic rays are particles from space that hit Earth with incredible energy. Some of these particles have so much energy that scientists are puzzled about where they come from. These ultra-high energy particles are much more powerful than anything we can create on Earth.
Origin Mysteries
The origin of cosmic rays is one of the biggest mysteries in space science. Researchers have many theories, but none can fully explain all the data. Some think they come from supernovae, while others suggest they might be from black holes or even unknown sources.
Detection Challenges
Detecting cosmic rays is not easy. They are rare and hard to catch. Scientists use special detectors placed deep underground or even in Antarctica to find them. NASA’s Fermi Space Telescope has also been used to look for these elusive particles, but it has not always been successful.
The search for cosmic rays is like looking for a needle in a haystack, but it’s a challenge that scientists are eager to take on.
Curious Pulsars
Pulsars are one of the most fascinating objects in space. These neutron stars rotate and emit lighthouse-like beams of electromagnetic energy. They are incredibly dense, often less than 20 miles wide, and can spin dozens or even hundreds of times per second. Let’s explore some of the curious aspects of these cosmic oddities.
Millisecond Pulsars
Millisecond pulsars are a special type of pulsar that spin at an astonishing rate, sometimes up to 700 times per second. This rapid rotation is due to the transfer of angular momentum from a companion star. These pulsars are incredibly precise, making them excellent cosmic clocks.
Magnetar Anomalies
Magnetars are a type of pulsar with extremely strong magnetic fields, trillions of times stronger than Earth’s. These magnetic fields can cause starquakes and release vast amounts of energy. The anomalies observed in magnetars challenge our understanding of physics and magnetic fields.
Binary Pulsar Systems
Binary pulsar systems consist of two stars orbiting each other, one of which is a pulsar. These systems are crucial for testing the theories of general relativity. The interaction between the two stars can lead to fascinating phenomena, such as the emission of gravitational waves.
Pulsars, with their rapid spins and intense magnetic fields, offer a new way for beneficial microbes to survive extreme conditions and space.
Odd Quasars
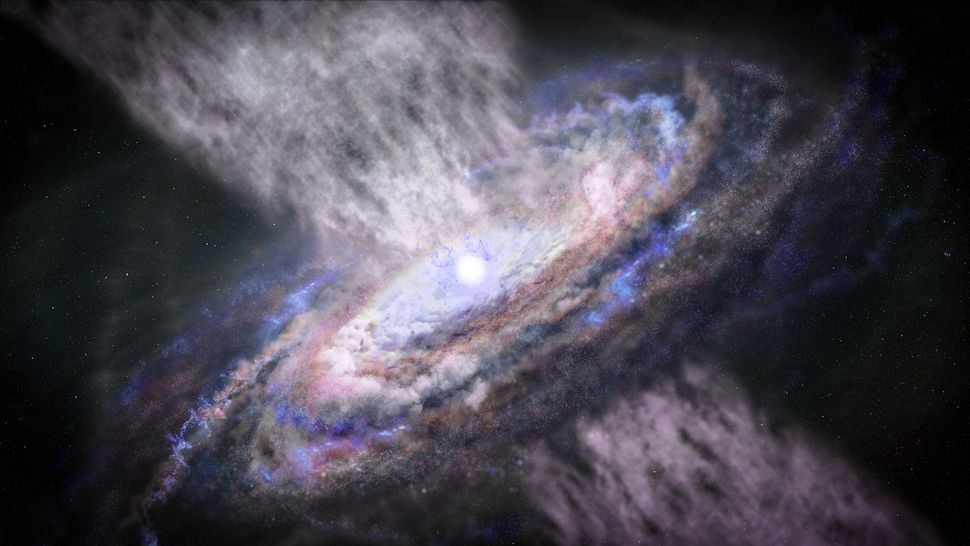

Blazar Phenomenon
Blazars are a type of quasar that emit powerful jets of energy directly towards Earth. These jets are so intense that they can outshine entire galaxies. Blazars are among the most energetic phenomena in the universe. They are fascinating because they help scientists understand the behavior of supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies.
Jet Collimation
The jets from quasars are incredibly narrow and focused, a process known as collimation. This collimation is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be influenced by magnetic fields. The jets can travel vast distances across space, sometimes spanning thousands of light-years. This phenomenon is one of the most outlandish objects in the universe.
Quasar Lifecycles
Quasars go through different stages in their lifecycles. Initially, they are very bright and active, but over time, they can become less luminous. This change is due to the amount of material the black hole consumes. Understanding these lifecycles helps scientists learn more about the evolution of galaxies and the universe itself.
Quasars are not just bright objects in the sky; they are key to unlocking the mysteries of the universe’s expansion and evolution.
Conclusion
The universe is full of strange and amazing things that challenge what we know. From the mysterious black holes that can stretch objects into spaghetti, to the odd quasars with their powerful jets, space never stops surprising us. Strange exoplanets, dark matter, and cosmic rays all add to the mystery. As we keep exploring, we will surely find even more weird and wonderful things out there. The more we learn, the more we realize how much we still don’t know. The adventure of discovery in space is just beginning, and who knows what we will find next?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an event horizon?
An event horizon is the boundary around a black hole beyond which nothing can escape, not even light.
How does Hawking radiation work?
Hawking radiation is a theoretical prediction that black holes emit radiation due to quantum effects near the event horizon.
What is spaghettification?
Spaghettification is the process where objects get stretched and torn apart by a black hole’s gravity.
What are hot Jupiters?
Hot Jupiters are gas giant exoplanets that orbit very close to their stars, making them extremely hot.
What is a diamond planet?
A diamond planet is a type of exoplanet that is thought to be composed largely of diamond, due to its high carbon content.
How do Tatooine-like systems work?
Tatooine-like systems have planets that orbit two stars, much like the fictional planet Tatooine in Star Wars.
What are WIMPs and axions?
WIMPs (Weakly Interacting Massive Particles) and axions are hypothetical particles that could make up dark matter.
What is gravitational lensing?
Gravitational lensing occurs when a massive object, like a galaxy, bends light from objects behind it, making them appear distorted or magnified.
