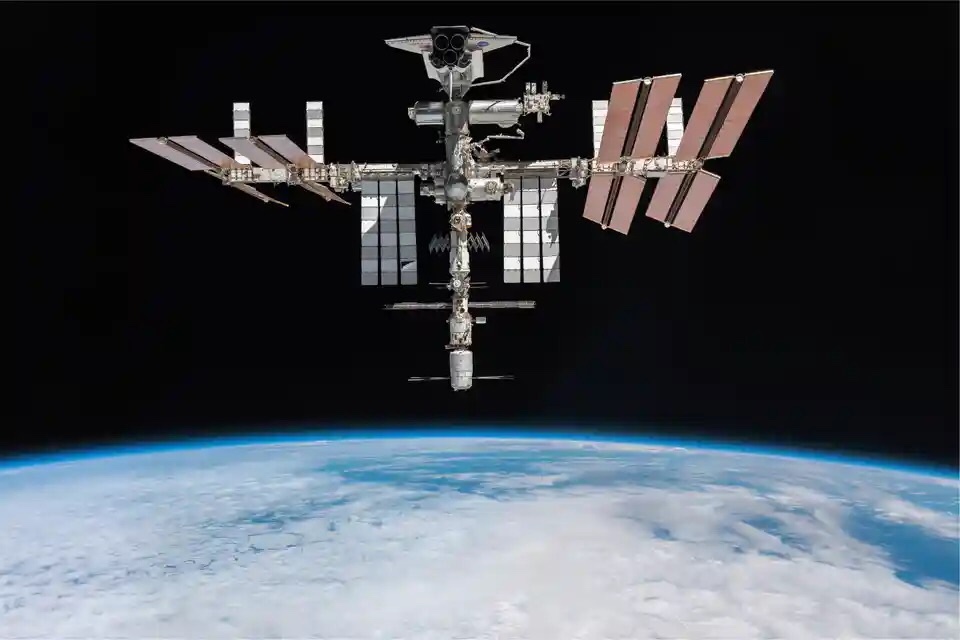
The International Space Station (ISS) stands as a shining example of human ingenuity, international cooperation, and a symbol of our unrelenting quest for knowledge beyond the boundaries of our planet. Orbiting over 250 miles above the Earth’s surface, the ISS is a testament to what can be achieved when nations come together to explore the cosmos.
The History and Development of the ISS
The journey of the ISS began in the 1990s, as a cooperative project involving multiple space agencies from around the world. The United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada all played critical roles in its development and construction.
The International Crew and Its Mission
The ISS hosts a unique, international crew representing various nations. Astronauts and cosmonauts live and work together in this confined space for extended periods, carrying out scientific experiments, maintaining the station, and preparing for future missions.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the inner workings of the ISS, exploring its living and working spaces, the scientific research conducted aboard, and the impact of this remarkable laboratory on space exploration. We will also touch on the challenges and experiences faced by the astronauts who call the ISS their temporary home.
Join us on this journey to unravel the story of the ISS, a global laboratory in space that has expanded our understanding of the cosmos and paved the way for humanity’s future among the stars.
The History and Development of the ISS
The story of the International Space Station (ISS) is one of international collaboration, visionary leadership, and scientific innovation. It represents a significant milestone in human space exploration, where multiple nations came together to create a space laboratory like no other.
A Vision of International Cooperation
The origins of the ISS can be traced back to the late 1980s and early 1990s when the world was witnessing the end of the Cold War. What emerged from this geopolitical shift was a remarkable opportunity for global cooperation in space. The United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada recognized the potential for a shared space station that could serve both scientific and diplomatic purposes.
In 1998, the Russian space station Mir had just completed its mission, and NASA’s space shuttle program was in full swing. The time was ripe for these nations to pool their resources and expertise to create a space station that would serve as a testament to diplomacy and the advancement of human knowledge.
Construction in Orbit
The ISS wasn’t built on Earth and launched as a complete structure. Rather, it was constructed in orbit, piece by piece, over several years. This complex process involved numerous missions, spacewalks, and shuttle launches, with each module and component designed to fit together like a giant cosmic puzzle.
Russia played a crucial role in providing the first modules, while NASA’s space shuttles ferried many components into orbit. The European Space Agency (ESA), the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) contributed vital components, further highlighting the global effort behind the ISS.
Continuous Collaboration
Since its inception, the ISS has been continuously inhabited by international astronauts, ensuring its constant operation. These astronauts live and work aboard the station, conducting experiments and maintaining its systems. Their presence emphasizes the station’s role as a hub for scientific research and international diplomacy.
The ISS has been home to more than just astronauts; it has hosted experiments across a wide range of scientific disciplines. From biology to physics, astronomy to environmental science, the ISS has become a global laboratory where researchers can conduct experiments in the unique microgravity environment of space.
This international collaboration is an example of how space exploration transcends borders and fosters cooperation for the advancement of science and technology. The ISS is not just a symbol of unity; it’s a symbol of what can be achieved when the world works together towards a common goal.
As we continue to explore the various facets of the ISS in this blog series, we’ll uncover more about the living conditions on the station, the scientific research conducted, and the invaluable contributions of the astronauts who call it home. The ISS truly stands as a testament to human ingenuity, international collaboration, and the unending quest for knowledge in the cosmos.
The International Crew and Its Mission
The International Space Station (ISS) orbits high above the Earth, but its true significance lies in the international crew that inhabits it. Comprising astronauts from diverse nations, the ISS serves as a shining example of how individuals from different cultures and backgrounds can come together to work in harmony for the greater good of scientific discovery.
A Global Team in Orbit
The crew of the ISS is truly international, with representatives from the various space agencies involved in its operation. This multinational approach is a testament to the collaborative spirit that underpins the station’s mission. Astronauts and cosmonauts from the United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada work side by side, transcending national boundaries in the pursuit of scientific knowledge.
A typical day on the ISS includes scientific experiments, maintenance tasks, exercise to counteract the effects of prolonged weightlessness, communication with mission control on Earth, and, of course, a few moments to gaze out of the station’s windows at our blue planet below.
These astronauts, also known as “spacefarers,” undergo rigorous training in their respective countries and then receive additional training to work in the unique microgravity environment of the ISS. They are selected for their expertise in various scientific fields, including biology, physics, chemistry, and engineering, ensuring they can conduct a wide range of experiments while on board.
Living in Space: The Daily Routine
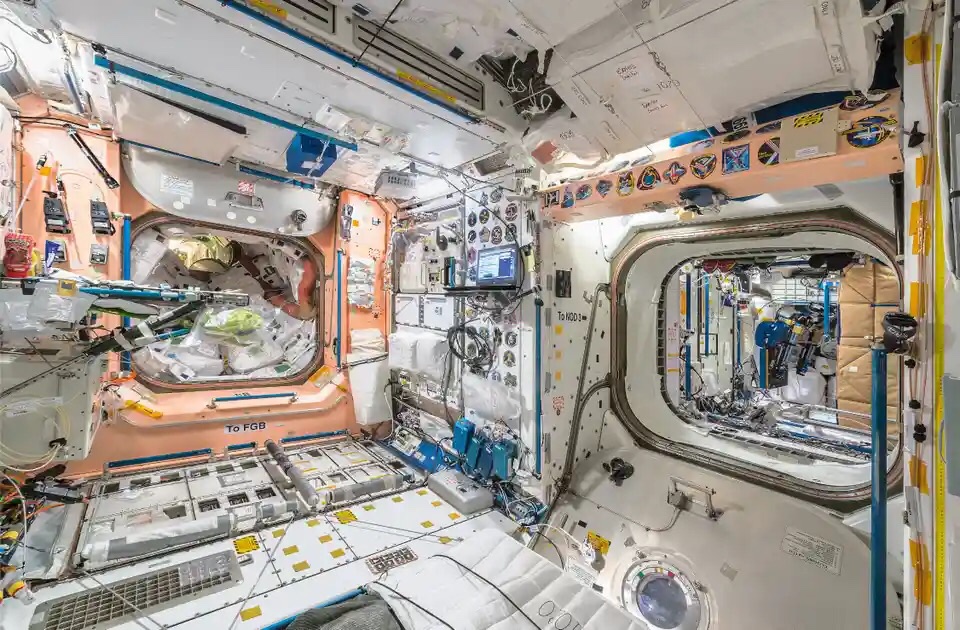

Living aboard the ISS is no ordinary experience. Astronauts and cosmonauts adapt to a life of zero gravity, where the familiar rules of up and down no longer apply. Their daily routine involves a carefully structured balance between work and personal time, which is essential for both their physical and mental well-being.
The Mission: Scientific Exploration and Diplomacy
The primary mission of the ISS is twofold: scientific exploration and international diplomacy. As a laboratory in space, the station hosts a wide array of experiments in fields such as biology, physics, and materials science. These experiments take advantage of the unique microgravity environment to advance our understanding of various scientific phenomena.
Furthermore, the ISS stands as a symbol of international collaboration and diplomacy. It showcases how nations can work together for the common goal of space exploration, transcending terrestrial conflicts and divisions.
Over the years, the ISS has become a testament to what can be achieved when countries unite in the pursuit of knowledge and the advancement of human space exploration. Its legacy extends far beyond its physical presence in orbit, demonstrating that humanity can reach beyond its own boundaries and explore the cosmos together.
In the following sections of this blog series, we will delve deeper into the inner workings of the ISS, exploring its living and working spaces, the scientific research conducted aboard, and the impact of this remarkable laboratory on space exploration. We will also touch on the challenges and experiences faced by the astronauts who call the ISS their temporary home. Join us as we continue our journey through this global laboratory in space.
ALSO READ: CHINA SENDING ZEBRAFISH TO TIANGONG SPACE STATION
Inside the ISS: The Living and Working Space
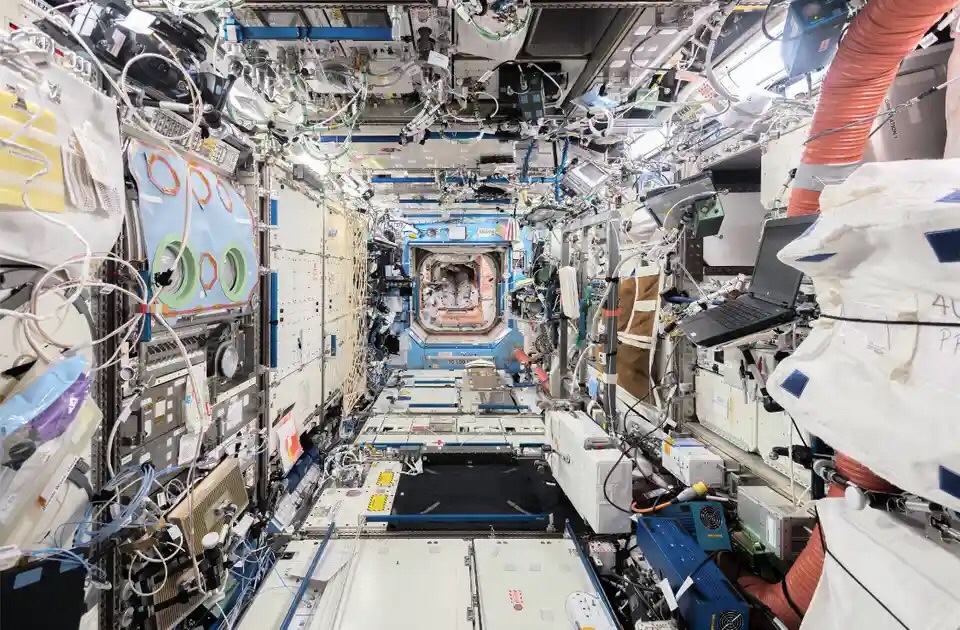

The ISS is an orbiting laboratory for conducting scientific and technological experiments in microgravity. It is an extraterrestrial base for learning how to live and work in a remote, isolated and confined environment to prepare for exploring other planets. It is also a home to the astronauts and cosmonauts there. Paolo Nespoli and Roland Miller’s book Interior Space: A Visual Exploration of the International Space Station is published by Damiani. All photographs courtesy of Nasa and ASI
Stepping inside the International Space Station (ISS) is like entering a world unlike any other. It’s a unique microgravity environment where astronauts live and work, conducting experiments, maintaining the station, and experiencing daily life that’s quite different from what we’re accustomed to on Earth.
The Space Station Layout
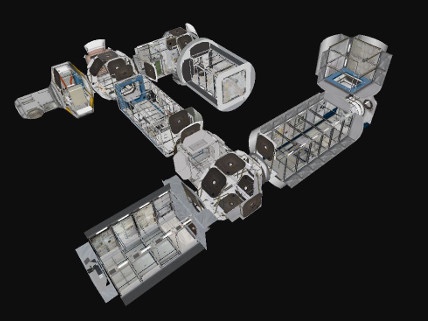
The ISS consists of multiple interconnected modules and components, each serving a specific purpose. These modules provide living quarters, laboratories, and support systems that make it possible for the astronauts to thrive in the harsh vacuum of space.
- The Living Quarters: The station includes sleeping quarters, hygiene facilities, and common areas where astronauts can relax and communicate with their loved ones on Earth. These areas are essential for maintaining their physical and mental well-being during long-duration missions.
- Laboratories: The ISS houses several laboratories where a wide range of experiments are conducted. The microgravity environment of the station allows scientists to investigate various phenomena, from fluid dynamics to biological processes, in ways that are impossible on Earth.
- Control Centers: The ISS has multiple control centers that help manage its systems and coordinate activities. These control centers are essential for ensuring the station’s smooth operation.
Microgravity Living
Living on the ISS means experiencing microgravity 24/7. This presents unique challenges and opportunities. In microgravity, everyday tasks like eating, drinking, and personal hygiene are quite different. Astronauts must learn how to adapt to these conditions.
- Eating and Drinking: In microgravity, food and drinks don’t fall to the ground; they float. Astronauts consume specially designed foods and use containers to avoid spills.
- Hygiene: Keeping clean is essential for astronaut health. The ISS is equipped with facilities for personal hygiene, including waterless shampoo, towelless body wash, and airflow toilets.
- Exercise: Prolonged microgravity can lead to muscle and bone loss, so astronauts engage in daily exercise routines using specialized equipment to stay physically fit.
The View from the Cupola
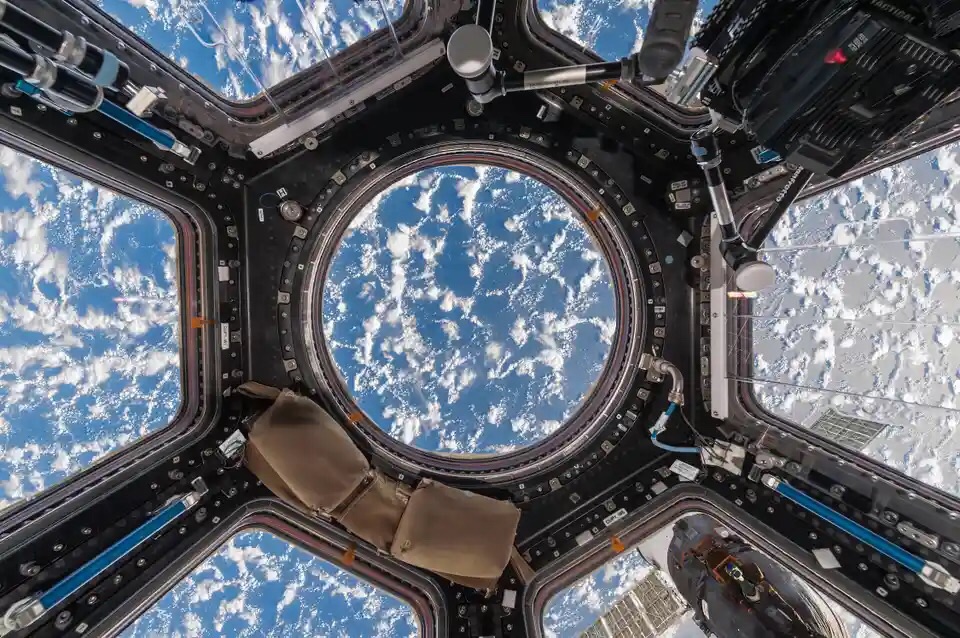

A stunning pattern of clouds and light over the ocean. The organic shapes of the clouds contrast with the geometric lines and shapes of the Cupola’s interior
Photograph: Paolo Nespoli and Roland Miller
One of the most remarkable spaces on the ISS is the Cupola, a module with seven windows that offer breathtaking views of Earth. This is where astronauts can take a moment to gaze at our planet, capturing images and memories of their unique vantage point.
Inside the ISS, every aspect of daily life has been carefully designed to ensure the safety and well-being of its crew, as well as the successful execution of scientific experiments. It’s a testament to human adaptability and the power of technology, allowing us to not only survive but thrive in the extreme environment of space.
In the upcoming sections of this blog series, we will explore the scientific research conducted aboard the ISS, the international partnerships that make it possible, and the impact of this space laboratory on our understanding of the cosmos and future space exploration. Join us as we continue our journey through this extraordinary laboratory in the stars.
Scientific Research on the ISS
The International Space Station (ISS) is more than just an impressive engineering feat and a symbol of international cooperation; it’s also a world-class laboratory for scientific research. With its unique microgravity environment and access to the vacuum of space, the ISS has become a hub for groundbreaking experiments that have far-reaching implications for science, technology, and our understanding of the universe.
Unlocking the Mysteries of Microgravity
One of the primary attractions of the ISS is its microgravity environment. This unique condition provides scientists with the ability to conduct experiments that are simply impossible on Earth. Some key areas of research include:
- Biological Studies: The ISS is a biological laboratory like no other. Scientists examine the effects of microgravity on living organisms, including humans. This research helps us understand bone density loss, muscle atrophy, and the impact of space travel on the human body.
- Materials Science: The microgravity environment allows researchers to grow large, pure crystals and investigate the properties of materials without the interference of gravity. This has led to advances in materials science, which have applications on Earth as well.
- Fluid Physics: Fluids behave differently in microgravity, and this provides insights into how fluids move and interact. This knowledge is invaluable for industries ranging from medicine to energy production.
Earth and Space Observation
The ISS is not just a laboratory for scientific experiments; it’s also an observatory. The station provides a unique vantage point for Earth observation, meteorological studies, and space exploration:
- Earth Observation: The ISS captures stunning imagery of our planet. Astronauts photograph natural disasters, climate changes, and other Earth phenomena. This data is vital for climate studies and disaster monitoring.
- Astronomy and Space Phenomena: The ISS provides a stable platform for telescopes. This allows for space observation free from the Earth’s atmosphere, improving our understanding of cosmic phenomena.
International Collaboration in Scientific Research
One of the remarkable aspects of the ISS is its multinational nature. A multitude of experiments from a wide range of scientific disciplines are conducted by researchers from around the world. The ISS transcends borders and fosters collaboration for the advancement of science and technology.
Applications Beyond Space
The research conducted on the ISS has significant implications on Earth. Scientific discoveries made in space can lead to advances in medicine, materials science, agriculture, and environmental protection. These applications underscore the importance of the ISS as a unique scientific platform.
As we delve deeper into the research conducted aboard the ISS in this blog series, we will explore specific experiments, their impact on various scientific fields, and the innovative technologies developed for use in space and back on our home planet. Join us in discovering the profound contributions of this orbital laboratory to the progress of science and humanity.
International Cooperation and Partnerships
The International Space Station (ISS) is a testament to the power of international cooperation and diplomacy. This remarkable space laboratory, orbiting over 250 miles above the Earth, is a symbol of what can be achieved when nations come together to explore the cosmos.
A United Global Effort
The idea for the ISS was born during a period of significant global change. The end of the Cold War created a unique opportunity for cooperation among nations that had previously been locked in a space race. The United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada recognized the potential for a shared space station that could serve both scientific and diplomatic purposes.
The Role of Key Nations
Each of the major spacefaring nations involved in the ISS project made invaluable contributions to its development:
- United States: NASA, the United States’ space agency, played a significant role in funding and coordinating the ISS project. The U.S. space shuttles were instrumental in transporting components into space.
- Russia: As a successor to the Soviet space program, Russia’s space agency, Roscosmos, provided essential modules, crew transportation, and experience from the previous space station, Mir.
- Europe: The European Space Agency (ESA) contributed the Columbus Laboratory and other modules. Europe’s involvement in the ISS program strengthened international cooperation.
- Japan: The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) delivered the Kibo laboratory, enhancing the station’s research capabilities.
- Canada: The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) provided the Canadarm and Canadarm2 robotic systems, which play critical roles in station operations.
The Assembly of a Space Marvel
The construction of the ISS was a monumental task. The station wasn’t built on Earth and launched as a complete structure; rather, it was assembled in orbit, piece by piece. This required multiple missions, spacewalks, and shuttle launches to transport and connect the various components. The international effort was evident at every step of this assembly process.
The Importance of Diplomacy
The ISS represents not only scientific advancement but also diplomacy in action. It has showcased how nations can set aside their differences and work together toward a common goal. The international crew aboard the ISS is a living testament to this collaboration, where astronauts from different countries live and work together for the greater good of humanity.
A Model for Future Space Exploration
The ISS has set the stage for future international cooperation in space exploration. As we plan missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, the lessons learned from the ISS program are guiding the way. The success of the station demonstrates that, even in a competitive world, countries can come together for the greater good of scientific discovery and space exploration.
In the upcoming sections of this blog series, we will delve deeper into the inner workings of the ISS, exploring the scientific research conducted aboard, the international partnerships that make it possible, and the impact of this remarkable laboratory on our understanding of the cosmos and future space exploration. Join us as we continue our journey through this global laboratory in space.
ALSO READ: SPACE TOURISM DREAMS: HOW CLOSE ARE WE TO VACATIONING IN SPACE?
Sustainability and Future of the ISS: A Cosmic Legacy
The International Space Station (ISS) is not just a laboratory in the stars; it’s a testament to human ingenuity and international cooperation. It has orbited Earth for over two decades, continuously expanding our understanding of science and fostering diplomacy among nations. As we explore the sustainability and future of the ISS, we uncover a legacy that reaches beyond its current mission.
A Remarkable Journey
Since its first module was launched into space in 1998, the ISS has been a beacon of human achievement. It’s not only the largest human-made structure in space but also a testament to the limitless potential of international collaboration. It has hosted astronauts from multiple countries, who have conducted experiments across various scientific disciplines.
Sustainability Challenges
As the ISS has aged, the challenges of maintaining its sustainability have become more apparent. The harsh environment of space, including exposure to radiation and micrometeoroids, takes its toll on the station’s structure and systems. Systems age, and replacements or repairs become necessary. This is where the station’s future sustainability comes into focus.
The Role of Commercial Partners
To ensure the ISS’s sustainability, a paradigm shift is underway. More and more, space agencies are turning to commercial partners for assistance in maintaining and operating the station. This approach not only eases the financial burden but also paves the way for a broader range of activities in space. Commercial companies are contributing resources and innovations that expand the ISS’s capabilities.
Science Continues
One of the most critical aspects of the ISS’s sustainability is its ongoing role as a space laboratory. It continues to be a hub for scientific research, hosting experiments that would be impossible to conduct on Earth. Microgravity research, Earth and space observation, and life sciences experiments are just a few of the fields contributing to our understanding of science and technology.
The Path to the Moon and Mars
The ISS also plays a pivotal role in preparing for future missions to the Moon and Mars. Lessons learned on the station are directly applicable to these missions. In many ways, the ISS serves as a stepping stone, testing technology and providing insights into the challenges of long-duration space travel.
The ISS in the Context of Space Exploration
The future of the ISS is not isolated but part of a broader context of space exploration. Its legacy includes the knowledge gained, the international partnerships fostered, and the path paved for commercial activities in space. As space agencies and commercial entities envision their roles in the future of space, the ISS remains a symbol of what can be achieved when countries unite for a common goal.
Continuing the Journey
As the ISS embarks on its third decade in space, its future is promising, with planned missions stretching well into the 2030s. Sustainability is at the heart of these plans, ensuring that the ISS continues to serve as a testament to human potential, global cooperation, and the unending quest for knowledge in the cosmos.
The International Space Station, with its rich legacy and ongoing contributions to science and diplomacy, will remain an enduring symbol of what humanity can achieve when it reaches for the stars together. It not only represents the past and present of space exploration but also offers hope for the bright future of cosmic discovery that lies ahead.
The Impact of the ISS on Space Exploration: A Cosmic Legacy
The International Space Station (ISS) is not just a laboratory in the stars; it’s a symbol of human achievement and international cooperation. Beyond its scientific contributions, the ISS has had a profound impact on space exploration and the way we envision humanity’s future among the stars. In this blog post, we’ll explore the lasting legacy of the ISS on the future of space exploration.
A Platform for Advancement
Since the launch of its first module in 1998, the ISS has been a hub for scientific research and technological advancements. The station’s microgravity environment has allowed scientists to conduct experiments across various fields, from biology and physics to materials science and environmental research. These experiments have yielded valuable data and insights that have applications not only in space but also back on Earth.
International Diplomacy
The ISS is more than a scientific platform; it’s a symbol of international cooperation. It has brought nations together, transcending geopolitical conflicts and fostering collaboration in space exploration. The station’s international crew is a living testament to this cooperation, showcasing how people from different backgrounds and nationalities can work together for the greater good.
Paving the Way for Future Missions
The ISS serves as a vital stepping stone for future exploration beyond low Earth orbit. Lessons learned on the station are directly applicable to missions to the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies. It provides a testbed for technologies, systems, and procedures that will be essential for these ambitious endeavors.
Commercial Opportunities
In recent years, the ISS has opened up to commercial partnerships, expanding its potential. Commercial companies are contributing resources and innovations to the station, further reducing the financial burden on space agencies and paving the way for a broader range of activities in space. This approach has the potential to stimulate economic growth in the space industry.
Training Ground for Astronauts
The ISS has served as a training ground for astronauts, providing valuable experience in long-duration spaceflight and spacewalks. This experience is crucial as space agencies plan for future missions that will require astronauts to spend extended periods in the challenging environments of the Moon and Mars.
Public Engagement
The ISS has captured the imagination of people around the world. Its missions, spacewalks, and Earth observations have been broadcast live, bringing space exploration closer to the public. It has inspired future generations to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) and has created a sense of unity and wonder as people gaze at our blue planet from space.
A Symbol of Hope and Cooperation
As we look to the future of space exploration, the ISS remains a symbol of hope and cooperation. It demonstrates what can be achieved when countries unite for a common goal, extending human presence beyond our home planet. Its enduring legacy is a reminder of the boundless potential of humanity as we continue our journey among the stars.
The International Space Station, with its rich legacy and ongoing contributions to science, diplomacy, and the future of space exploration, will remain an enduring symbol of what humanity can achieve when it reaches for the stars together. It not only represents the past and present of space exploration but also offers hope for the bright future of cosmic discovery that lies ahead.
The Human Element: Astronaut Experiences and Challenges
The International Space Station (ISS) isn’t just an extraordinary engineering achievement or a center for scientific research; it’s a home in the stars. Astronauts, the brave individuals who live and work aboard the ISS, experience a unique and challenging existence, unlike any other profession on Earth. In this blog post, we’ll explore the human element of the ISS, delving into the experiences, challenges, and rewards of life in space.
Astronaut Selection and Training
Becoming an astronaut is a monumental achievement in itself. The selection process is highly competitive, and astronauts undergo rigorous training. Their training covers everything from spacecraft systems and spacewalk procedures to scientific experiments and personal health in microgravity. They must be prepared to handle any situation that might arise during their mission.
ALSO READ : ASTRONAUTS WHO DIED IN SPACE: A LOOK AT THE HISTORY AND LEGACY OF THESE TRAGIC EVENTS
Life in Microgravity
One of the most obvious challenges astronauts face is the absence of gravity. Microgravity can take some time to adapt to, and it affects everything from movement and daily tasks to bodily functions. Eating, drinking, and personal hygiene all require adjustments. Astronauts often remark on the joy of floating but also the challenges of living without the natural forces that govern life on Earth.
Astronaut Routines
A typical day for an astronaut is carefully structured to ensure they remain healthy and productive. The schedule includes time for scientific experiments, station maintenance, exercise to combat muscle and bone loss, and communication with mission control and loved ones on Earth. Astronauts even have the luxury of gazing at our planet through the station’s windows.
Spacewalks
Astronauts also engage in spacewalks, or extravehicular activities (EVAs). These are some of the most visually stunning moments of a space mission, but they are also some of the most physically and mentally challenging. Astronauts must be meticulous and coordinated as they perform maintenance and repairs on the exterior of the station while floating in the vacuum of space.
Isolation and Distance
The ISS is a closed environment, and astronauts can’t step outside for a breath of fresh air. They are isolated from the world, living and working with the same small group of individuals for months. This isolation, combined with the distance from Earth, can have psychological effects. Space agencies have procedures and support systems in place to help astronauts deal with these challenges.
The Rewards of Space Exploration
Despite the challenges, astronauts often describe their experiences as transformative and deeply rewarding. They get to be part of scientific breakthroughs, contribute to our understanding of the universe, and be part of a tradition of human exploration. The view from the Cupola, the station’s observation module, offers breathtaking vistas of our home planet and a profound sense of connection to the cosmos.
The human element is an integral part of the ISS, and astronauts who have called the station home are the embodiment of courage, determination, and curiosity. Their experiences and challenges not only push the boundaries of what we can achieve in space but also inspire the rest of us to reach for the stars. The ISS, with its international crew and their incredible stories, is a testament to the human spirit of exploration and discovery.
ALSO READ : DISCOVERING NEW FRONTIERS: THE FUTURE OF SPACE TRAVEL
Conclusion
The International Space Station (ISS) is more than a laboratory in the stars. It’s a testament to human ingenuity, international cooperation, and the unrelenting human spirit that constantly seeks to explore the cosmos. As we’ve journeyed through the various facets of the ISS in this blog series, we’ve uncovered the depth of its impact on science, diplomacy, and the future of space exploration.
The ISS, as a platform for scientific research, has provided insights into biology, materials science, and fluid physics that have applications both in space and on Earth. Its microgravity environment has allowed experiments that were previously unimaginable, opening new frontiers in scientific discovery.
This space station is not just a symbol of international diplomacy; it’s a living example of nations coming together to transcend political boundaries and collaborate for the common good. The ISS’s international crew, working harmoniously in an environment of shared exploration, is a testament to what can be achieved when we unite around a common goal.
The ISS serves as a stepping stone for future missions, offering essential experience and lessons that will be invaluable as we plan for missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. It’s not just a scientific platform; it’s a testbed for the technology and systems required for these ambitious endeavors.
The ISS has not only advanced science and diplomacy; it has also inspired generations. Its live broadcasts and breathtaking images of Earth from space have captured the imagination of people around the world, igniting interest in science, technology, and space exploration. It has kindled a sense of unity and wonder as people gaze at our fragile blue planet against the backdrop of the cosmos.
As the ISS continues its mission in the decades ahead, its legacy will live on, reminding us of humanity’s limitless potential when we work together to explore the stars. It represents hope, international cooperation, and the never-ending quest for knowledge throughout the universe.
The International Space Station, with its rich legacy and ongoing contributions to science, diplomacy, and the future of space exploration, is more than just a scientific laboratory; it’s a testament to what humanity can achieve when it reaches for the stars together. It not only represents the past and present of space exploration but also offers hope for the bright future of cosmic discovery that lies ahead.
