Imagine a star so big that it makes our Sun look like a tiny speck of dust. That’s UY Scuti, currently known as the largest star in our universe. In this article, we’ll explore this cosmic giant and try to understand just how enormous it really is.
How Do We Find and Measure Huge Stars?
Before we dive into UY Scuti, let’s talk about how astronomers find and measure stars that are so far away.
Measuring Stars from Earth
Astronomers use several clever methods to figure out how big stars are:
- Direct Imaging: Using powerful telescopes to actually see the star.
- Interferometry: Combining light from multiple telescopes to see more detail.
- Eclipsing Binary Systems: Watching how stars in pairs block each other’s light.
- Spectroscopic Analysis: Studying the colors of light coming from stars.
These tools help scientists estimate star sizes, even when they’re millions of light-years away.
A Quick History of Big Star Discoveries
The quest to find the largest stars in the universe has been ongoing for centuries. As our technology and understanding have improved, we’ve discovered increasingly massive stars:
- 1837: Epsilon Aurigae was recognized as an exceptionally large star.
- 1930s: VV Cephei was identified as one of the largest known stars.
- 2000s: VY Canis Majoris held the title of the largest known star for several years.
- 2012: UY Scuti was identified as potentially larger than VY Canis Majoris.
This ongoing search highlights the dynamic nature of astronomical research and our ever-expanding knowledge of the cosmos.
Why Studying Big Stars Matters
Understanding huge stars like UY Scuti is important because:
- It helps us learn how stars are born, live, and die.
- Big stars create many of the elements we find in the universe.
- They affect how galaxies form and change.
- Studying them pushes what we know about physics to the limit.
Meet UY Scuti: Our Current Record Holder

Now that we’ve set the stage, let’s turn our attention to the star of the show: UY Scuti. This celestial colossus has captured the imagination of astronomers and space enthusiasts alike since its discovery.
Basic Facts About UY Scuti
UY Scuti was first cataloged in 1860 by German astronomers at the Bonn Observatory. However, its true nature as an exceptionally large star wasn’t recognized until much later. Here are some key facts about UY Scuti:
- Designation: BD-12 5055
- Right Ascension: 18h 27m 36.53s
- Declination: -12° 27′ 58.9″
- Distance from Earth: Approximately 9,500 light-years
What Kind of Star is UY Scuti?
UY Scuti belongs to a rare class of stars known as hypergiants. These are among the most massive and luminous stars in the universe. Specifically, UY Scuti is classified as a red hypergiant, characterized by:
- Extremely large size
- High luminosity
- Cool surface temperature (for a star)
- Significant mass loss through stellar winds
This classification puts UY Scuti in an elite group of stars that push the boundaries of stellar physics.
How Big is UY Scuti Really?
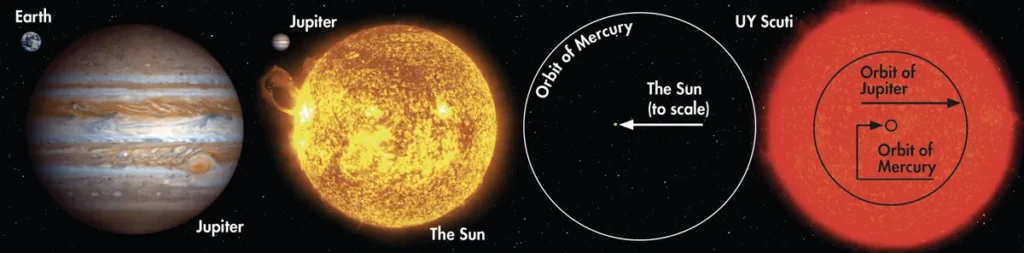
To truly appreciate the enormity of UY Scuti, we need to compare it to more familiar celestial objects.
Compared to Our Sun
- UY Scuti’s radius (distance from its center to its edge) is about 1,700 times bigger than the Sun’s.
- If UY Scuti were placed at the center of our solar system, its surface would extend beyond Jupiter’s orbit.
- The volume of UY Scuti could contain billions of Suns.
An Easy-to-Imagine Comparison
To put this into a more relatable perspective, consider this analogy:
If the Sun were the size of a golf ball (about 4.3 cm in diameter):
- Earth would be a tiny grain of sand about 4.6 meters away.
- UY Scuti, in comparison, would tower over this scene at a height of about 7,300 meters – nearly as tall as Mount Everest!
This analogy helps us grasp the truly astronomical scale we’re dealing with when discussing UY Scuti.
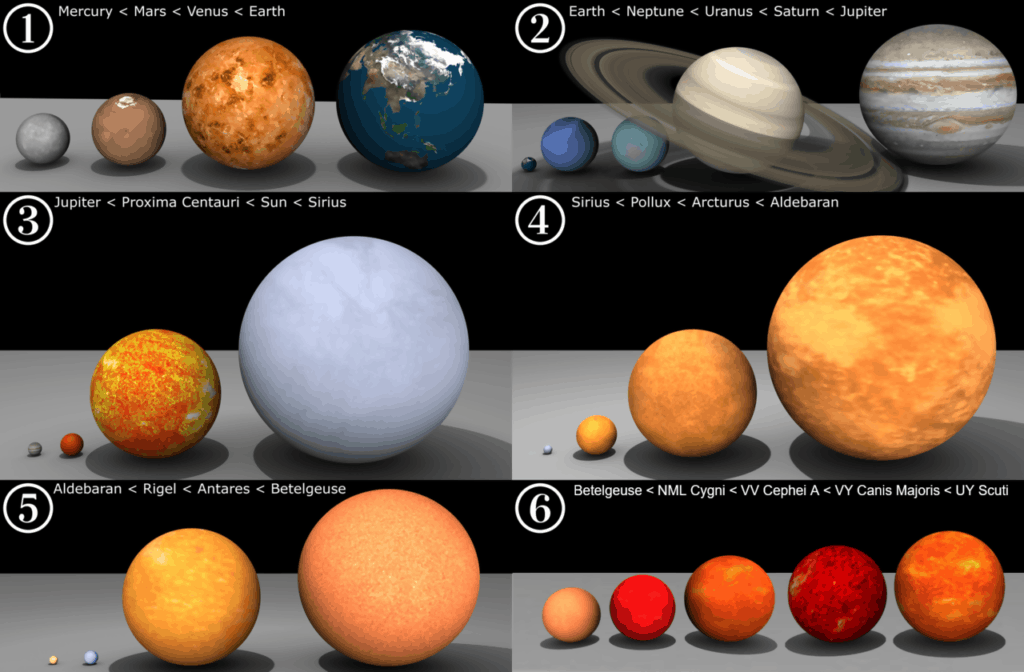
How It Stacks Up to Other Big Stars
UY Scuti is bigger than famous large stars like:
- Betelgeuse (in Orion): UY Scuti is 1.5 times larger.
- Antares (in Scorpius): UY Scuti is 2.5 times larger.
- VY Canis Majoris (once thought to be the biggest): UY Scuti is slightly larger, though the exact difference is subject to ongoing research.
Cool Facts About UY Scuti
UY Scuti isn’t just big – it has other interesting features too.
It’s Big, But Not the Heaviest
Interestingly, while UY Scuti holds the title for the largest known star in terms of volume, it’s not the most massive. Current estimates place its mass at about 7-10 times that of our Sun. This discrepancy between size and mass is due to its extremely low density – UY Scuti’s outer layers are so diffuse that they’re more akin to a hot vacuum than what we typically think of as stellar material.
The most massive stars known, such as R136a1 in the Large Magellanic Cloud, can have masses over 100 times that of our Sun, despite being much smaller in volume than UY Scuti.
Temperature and Brightness
Despite its enormous size, UY Scuti’s surface temperature is relatively cool for a star:
- Surface temperature: Approximately 3,365 K (3,092°C or 5,597°F)
- For comparison, our Sun’s surface temperature is about 5,778 K
However, due to its immense size, UY Scuti’s total luminosity is staggering:
- Luminosity: Estimated at 340,000 times that of the Sun
- This means UY Scuti emits more energy in one second than our Sun does in several days
UY Scuti’s Lifespan
Big stars like UY Scuti don’t live as long as smaller stars:
- It’s probably less than 10 million years old.
- It might only live for about 40 million years total.
- Our Sun, which is much smaller, is already 4.6 billion years old and will live for another 5 billion years.
Why It’s Hard to Measure Stars Like UY Scuti

Measuring huge, faraway stars is tricky:
- They’re very far away, making them hard to see clearly.
- Earth’s air can distort our view.
- These stars often change in size and brightness.
UY Scuti itself pulses, getting bigger and smaller over time. Its outer layers are so thin, it’s hard to tell where the star actually ends!
Other Stars That Might Be Even Bigger
While UY Scuti is the current record holder, there might be even bigger stars out there:
VY Canis Majoris: The Former Record Holder
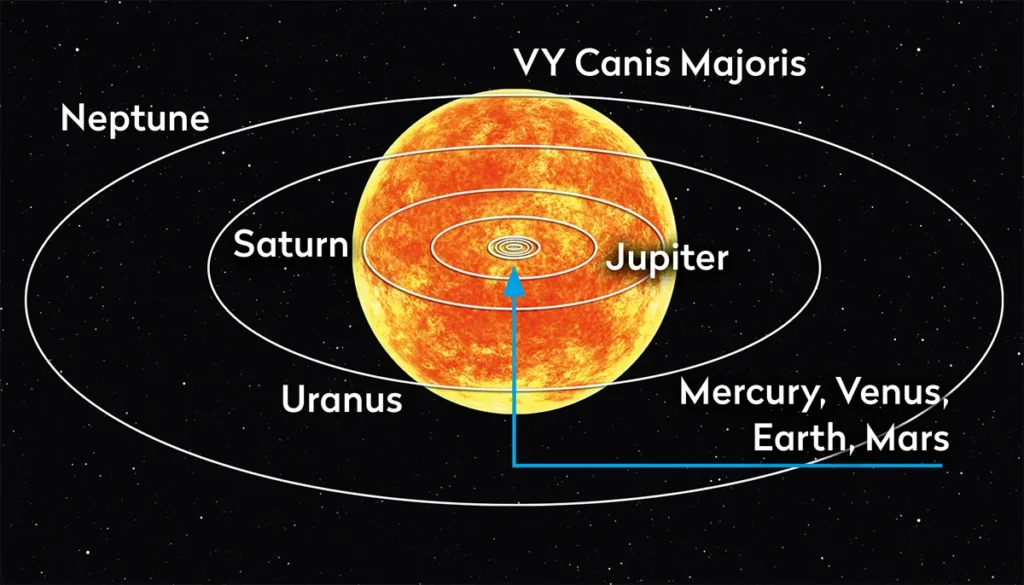
Before UY Scuti took the spotlight, VY Canis Majoris was widely considered the largest known star:
- Location: Constellation Canis Major
- Classification: Red hypergiant
- Estimated radius: 1,420 to 2,100 times that of the Sun
- Notable feature: Extensive circumstellar envelope
The uncertainty in its size measurements means it could potentially be larger than UY Scuti, highlighting the ongoing nature of this astronomical competition.
Stephenson 2-18: A Potential Rival to UY Scuti
A relatively recent addition to the list of enormous stars is Stephenson 2-18:
- Location: Scutum constellation, part of the Stephenson 2 cluster
- Classification: Red supergiant
- Estimated radius: Potentially up to 2,150 times that of the Sun
- Notable feature: One of the most luminous cool hypergiant stars known
Some studies suggest that Stephenson 2-18 could be even larger than UY Scuti, though more research is needed to confirm these measurements.
What Will Happen to UY Scuti in the Future?
As we’ve explored the current state and properties of UY Scuti, it’s natural to wonder about its future. What fate awaits this stellar giant, and what can it teach us about the life cycles of massive stars?
A Huge Explosion
- In the next million years or so, UY Scuti will likely explode as a supernova.
- This explosion will be so bright it could outshine entire galaxies for a short time!
After the Explosion
After it explodes, UY Scuti might:
- Become a black hole, if enough of it is left over.
- Turn into a super-dense neutron star.
- Or maybe even be completely destroyed, leaving nothing behind.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our journey on UY Scuti, let’s take a moment to look at what we’ve discovered. This enormous star, with its mind-boggling size and fascinating properties, is more than just a record-holder in the universe – it’s a gateway to understanding the incredible diversity and scale of our cosmic home.
UY Scuti teaches us that the universe is full of surprises. Just when we think we’ve grasped how big things can get, we find something even more enormous. This star challenges what we thought was possible and pushes scientists to rethink their theories about how stars form and evolve.
